Law
In the debates around the need to expand the rights that accrue through marriage to same-sex couples, what is often lost are the forms of legal recognition of relationships not in the nature of marriage or blood. As the nature of traditional relationships changes across India, with more people opting to live singly or with friends, we really need to begin thinking seriously about new forms of legal recognition.
Often, these marriages are performed in great haste as the groom comes to India for a short holiday. In their enthusiasm to clinch, what appears to be a highly desirable marriage alliance, which will open up new opportunities, exposure and happiness to their daughter, the parents may throw caution to the wind and seal the match.
A year ago, just ten minutes after I had landed in the Punjab and Haryana High Court. I was introduced to this young lawyer – not the least bit enthusiastic, a big critic of the law, of lawyers, of the High Court, and most importantly, of women. “Let me tell you a secret: law is not a profession for girls,” said he.
The Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act, 2012 (POCSO Act), defines a ‘child’ to mean ‘any person below the…
By: Diksha Sanyal at the JILS Blog The National Legal Services Authority v. Union of India [Writ Petition (Civil) No. 400 of 2012] has…
I graduated from a Law School in Bangalore in 2012 and moved back to my hometown, Lucknow, U.P., where I…
Chandra Deo Singh, a name not necessarily familiar to many of us, spent time in prison in1945 for taking part…
I am a perverse nomad. My journey encompasses cruising parks in Kolkata and New York City, friendships with didis of…
Any desire, not necessarily or narrowly sexual, but perhaps related to sexuality, such as independence, equality, gender role-bending, controlling your own finances, eating the food you’d like to eat as opposed to the food your spouse desires, wearing the clothes you’d like to wear, birth control, choosing to have or not to have children … any of these desires would have only that importance that the individual concerned is able to apportion to it.
On Jan 1, 2014 when I met Vidya Reddy, one of TULIR’s co-founders, for an interview on consent among teenagers…
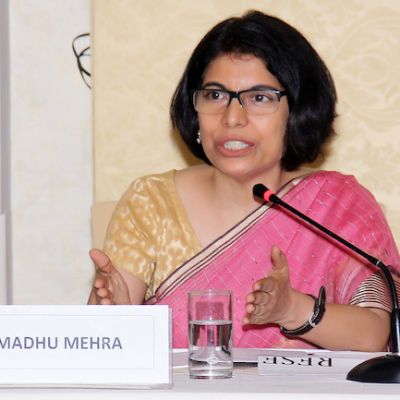
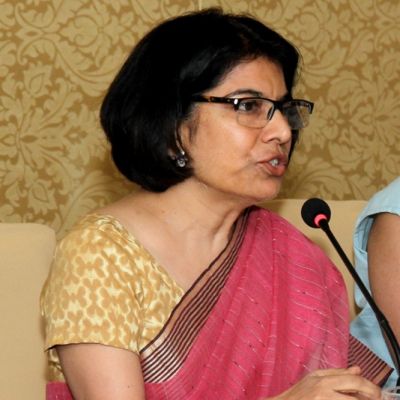
In this issue of In Plainspeak, we interview Madhu Mehra, lawyer and feminist activist. She is a founding member and the Executive Director of Partners for Law in Development (PLD), a legal resource group on women’s rights.
Disabled people might not have many spaces where they can speak openly about their sexual experiences or even sexual curiosity. There is a heavy monitoring of disabled young people especially, and this can mean that exploration, which is often how many of us discover sexuality, can be limited. Moreover, since the experiences of disabled people are not seen in popular media such as films, we can (and probably do) imagine we will have the same or similar experiences as non-disabled people – which is often not possible.
JG: As a founder member of The Alternative Law Forum (ALF) you have engaged with conventional law and at the…
I think that the level of power that law makers, opinion builders and stakeholders wield over the more vulnerable and younger people in society is enormous. Yet, these actors have chosen to focus only on building a policy regime of sexual violence, even to the extent of allowing juvenile offenders to be treated as adult accused – without any corresponding effort to build a sex positive culture within which they may exercise agency.