Sexuality
What is fiction? Is it born of reality? Or does it birth reality, reflecting it back at me until I see the things I do not see? Until I find the person that is me? Until I dance my horse dance under moon, under stars, in a room full of people who like horse dancing just as much as they like the swirly skirt and the pot-bellied person doing the Bhangra.
Both fiction and non-fiction are capable of great complexity if the making is in the hands of someone capable and complex. I have always held that good films – fiction, non-fiction or hybrid– emerge not from a familiarity with the subject, though that’s essential – but an understanding of the language of cinema.
We can speak of many situations in terms of access or its lack for all kinds of people, and it will always give us insight into the society we live in in two interdependent ways: one, it reveals a polarity between who is given and who is denied access, and two, it determines the big-picture human value given to the commodity that the access is contested for.
I thought of myself as a feminist activist much before I formally entered the development sector space. I participated in…
As a 17 year old who grew up in a relatively liberal Indian household, I should probably be proud of…
Accessibility begins with access, enabled or denied, to concepts and ideas. At the core, beyond the architecture of the real and virtual worlds, it is about the architecture of the ways in which this access is broadened, to not only accommodate, but to nurture, the myriad expressions of human minds and bodies.
There are many ways to be queer. Apart from the fact that queerness encompasses a wide variety of sexual expression,…
To belong or not to belong? Some people define themselves through commonalities. There are some who define themselves through difference and then seek to find others who share that difference. They find commonality in a shared difference. Commonality is what makes for a community. To keep that commonality becomes an unwritten rule. What lets you in? What keeps you out? Every community tries to keep its members together. There are expectations, rules, impositions and, for the dissidents, punishments. Ironically, even communities of people who do not conform to mainstream norms of sexuality or gender have their own norms.
Shikha Aleya: What are some of the biggest barriers you have faced in your efforts to create dialogue and visibilise…
After writing the words “Community and Sexuality” as the working title of this piece, I attempted to begin writing many…
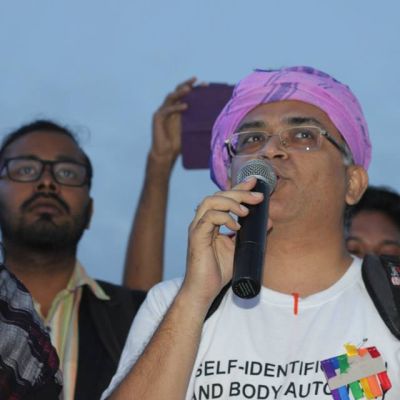
In this issue of In Plainspeak, we interview Pawan Dhall, Founding Trustee of Varta Trust, queer activist, writer and social researcher. He is also the editor of the Varta webzine, promoting and sustaining dialogue on gender and sexuality, across diverse groups of people. As Pawan says, “We are all strung together on a spectrum of gender and sexuality, and we don’t have to be fixed at a single point on the spectrum throughout our lives.”
Our desire to connect is perhaps one of the human aspirations that both Sexuality and the Internet serve. And with the Internet we now have new ways, unthought of even twenty years ago, of connecting with each other, and even at times with ourselves, finding aspects of our selves that we did not know existed.
Online dating websites and apps are one of those technological innovations that people did not think would ever do well….
The promises of the Internet are, of course, highly contextual. The Internet will mean very different things to a person who has access to their own mobile phone in a city with a reliable and affordable broadband or WiFi connection, as compared to someone who does not have access to a reliable Internet connection or who is unable to go to a shop to exchange downloaded songs and clips through an SD card.
The bill exhibits a lack of understanding of agency which ought to be given to a woman; that a woman should be able to make decisions when the question is with regard to her body. There is no need for the State to be the Big Brother.